In my last post, we explored how to set up a OpenWRT VM in VirtualBox.
Let's give it some clients! Since the router is using a intnets we need to configure some machines to use that as their primary way to connect to the internet.
Since Vagrant has support for multi-machine configurations and gives us minimal builds of machines, we'll use this for our clients.
The Plan
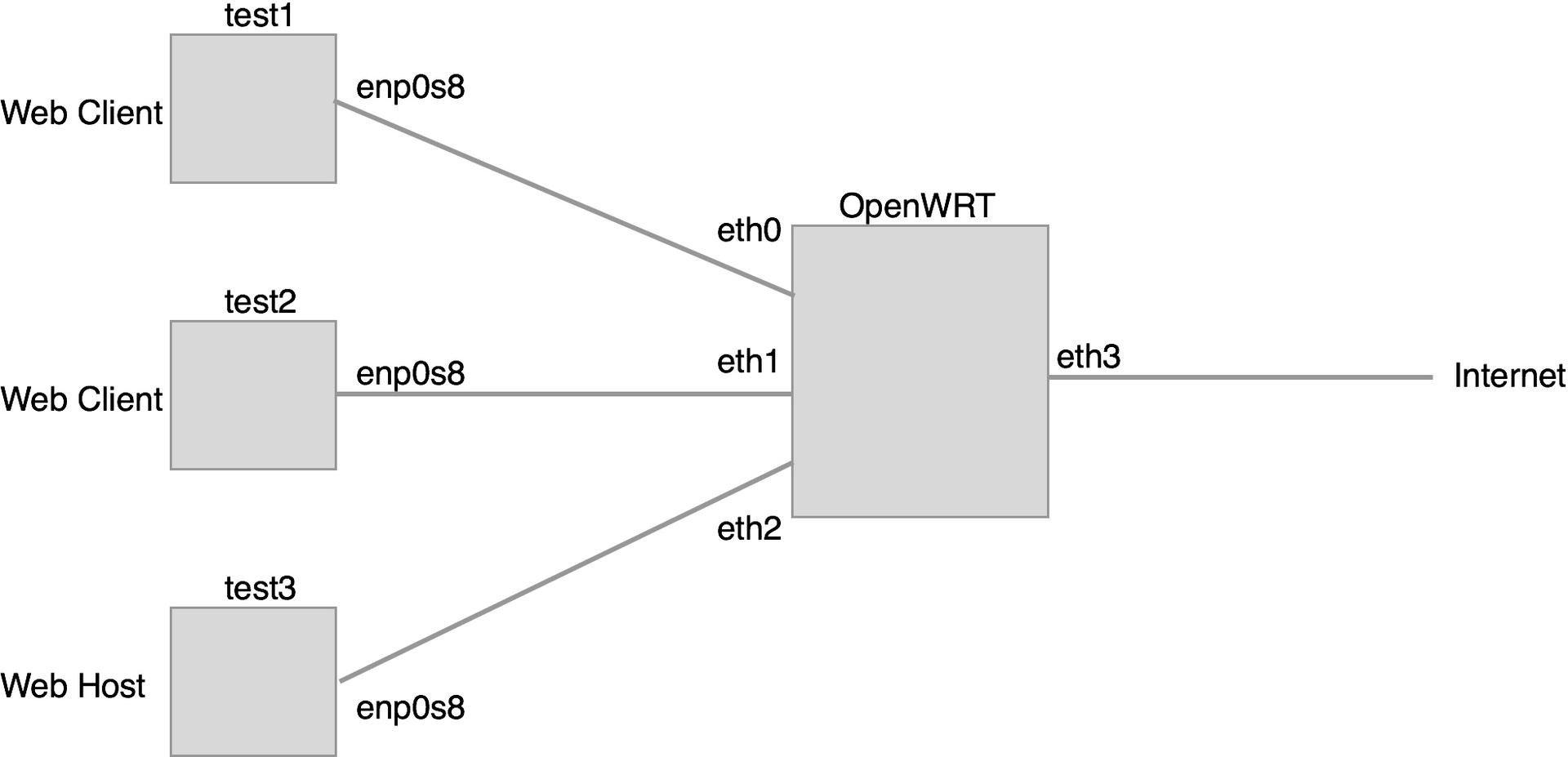
Here is (roughly) the goal. The pair of VMs test1 and test2 will access test3 (and the internet) through the OpenWRT router we created. Later, we'll build in QoS and talk about the effects of various parameters.
Getting started with Vagrant
I'll assume you've already install Vagrant. Let's make a workspace and set some enviroment variables. You might want to change this.
INTNET="openwrt"
WORKSPACE="workspace"
mkdir $WORKSPACE && \
cd $WORKSPACENext we'll write a Vagrantfile to orchestrate the boxes and give them various traits.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.define :test1 do |box|
box.vm.box = "chef/fedora-20"
box.vm.network "private_network",
type: "dhcp",
virtualbox__intnet: "port1"
end
config.vm.define :test2 do |box|
box.vm.box = "chef/fedora-20"
box.vm.network "private_network",
type: "dhcp",
virtualbox__intnet: "port2"
end
config.vm.define :test3 do |box|
box.vm.box = "chef/fedora-20"
box.vm.network "private_network",
type: "dhcp",
virtualbox__intnet: "port3"
end
endNow you can run it:
vagrant upBecause of how we configured the dhcp service on our OpenWRT router, these machine should connect primarily to the OpenWRT router over the NAT (falling back on it if things fail).
To check, access the VM's and ensure that the interface enp0s8 exists and has an inet address. For example, if I use vagrant ssh test1, then run the following, my outputs show I am assigned 192.168.1.196 by the OpenWRT router.
ifconfig enp0s8
# enp0s8: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
# inet 192.168.1.196 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255
# inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe31:dcfe prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
# inet6 fdca:27bb:4407::8a1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x0<global>
# inet6 fdca:27bb:4407:0:a00:27ff:fe31:dcfe prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x0<global>
# ether 08:00:27:31:dc:fe txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
# RX packets 16 bytes 2584 (2.5 KiB)
# RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
# TX packets 29 bytes 3722 (3.6 KiB)
# TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
route
# Kernel IP routing table
# Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
# default 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 enp0s8
# default 10.0.2.2 0.0.0.0 UG 1024 0 0 p2p1
# 10.0.2.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 p2p1
# link-local 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1003 0 0 enp0s8
# 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 enp0s8I should be able to access this from another VM if I use vagrant ssh test2 then run:
ping 192.168.1.196Fantastic. This means all of our machines can talk.
What's more, is that these three client machines will all talk to the internet through the router. You can, for example, wget something and watch in ifconfig enp0s8 as the TX and RX change.
Configuring a Host
In order to configure test3 to be a proper web host for our tests, it needs two things:
- A web server.
- Something (large) to serve.
Why something large? We'll be using emulated network interfaces that should be blazing fast, so having something large is key.
The easiest way to accomplish this is to have a large file on your VM host which is in the $WORKSPACE folder, this can then be shared with test3, which it can serve. This is because Vagrant automatically shares anything in the current directory into the VM's /vagrant folder.
Modify your Vagrantfile to match the following:
$make_host = <<SCRIPT
yum install -y nginx
sed -i 's/root .*/root \\/vagrant;/' /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
systemctl enable nginx
systemctl start nginx
SCRIPT
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.define :test1 do |box|
box.vm.box = "chef/fedora-20"
box.vm.network "private_network",
type: "dhcp",
virtualbox__intnet: "port1"
end
config.vm.define :test2 do |box|
box.vm.box = "chef/fedora-20"
box.vm.network "private_network",
type: "dhcp",
virtualbox__intnet: "port2"
end
config.vm.define :test3 do |box|
box.vm.box = "chef/fedora-20"
box.vm.network "private_network",
type: "dhcp",
virtualbox__intnet: "port3"
box.vm.provision "shell", inline: $make_host
end
endNow you should be able to fetch the IP address of test3 by SSH'ing into the box with vagrant ssh test3 then running ip addr show enp0s8 | grep 192.168. Mine is 192.168.3.201, yours might be different, substitute this where you see $TEST3IP.
On your test1 or test2 box, you should be able to do:
curl $TEST3IP/VagrantfileThe output of this command should be the script we wrote. Your next step should be to find a file of sufficient size. If you're stuck on ideas, there is an hour long video of a Norwegian train trip which would be suitable.
On test3:
yum install -y youtube-dl
youtube-dl https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m7rWhCqsh2I -o /vagrant/video.mp4The resulting file is approximately 1.18GB, which is enough for our use.
You can test with:
curl $TEST3IP/video.mp4Quality of Service
Now that we have a small network set up with our router, the next step is configuring the quality of service on the router. I discuss this here.